Interval Walking for Weight Loss: A Comprehensive Guide to the Japanese 3x3 Method and Beyond
Interval Walking to Lose Weight: Japanese Walking
Interval walking represents a revolutionary approach to fitness that transforms ordinary walking into a highly effective weight loss strategy. Unlike traditional steady-pace walking, this method alternates between periods of brisk, high-intensity walking and slower recovery phases, creating a metabolic boost that can accelerate fat burning and improve cardiovascular health. Research demonstrates that interval walking can produce weight loss results that are 40% greater than continuous moderate-intensity walking, while requiring less total exercise time and being gentler on joints than high-impact activities. This evidence-based approach originated in Japan and has gained widespread recognition for its accessibility, effectiveness, and sustainability for people of all fitness levels.
Understanding Interval Walking Training: The Science Behind the Method
Interval Walking Training (IWT) fundamentally operates on the principle of alternating metabolic demands to create superior physiological adaptations compared to steady-state exercise. The core mechanism involves pushing the cardiovascular system to work at approximately 70-85% of maximum aerobic capacity during high-intensity phases, followed by recovery periods at 40-50% capacity. This fluctuation creates what exercise physiologists term "excess post-exercise oxygen consumption" (EPOC), whereby the body continues burning calories at an elevated rate for up to 24 hours after completing the workout.

30-day outdoor workout plan combining walk/run intervals with strength exercises to enhance fitness.
The Japanese 3x3 method, developed by Dr. Hiroshi Nose at Shinshu University, represents the most thoroughly researched interval walking protocol. This approach consists of alternating 3 minutes of brisk walking at approximately 70% of peak aerobic capacity with 3 minutes of slower walking at 40% capacity, repeated five times for a total duration of 30 minutes. The protocol is designed to be performed 4-5 times per week, making it both time-efficient and sustainable for long-term adherence.
Research published in *Mayo Clinic Proceedings* demonstrates that participants following this protocol experience remarkable improvements across multiple health markers. Physical fitness increases by approximately 20%, including significant gains in maximal aerobic power and thigh muscle strength. Simultaneously, symptoms of lifestyle-related diseases such as hypertension, hyperglycemia, and obesity decrease by about 20%. These benefits extend beyond physical health, with participants reporting substantial improvements in mental health, including depression scores that dropped by 50%.
Weight Loss Effectiveness: Research-Based Evidence
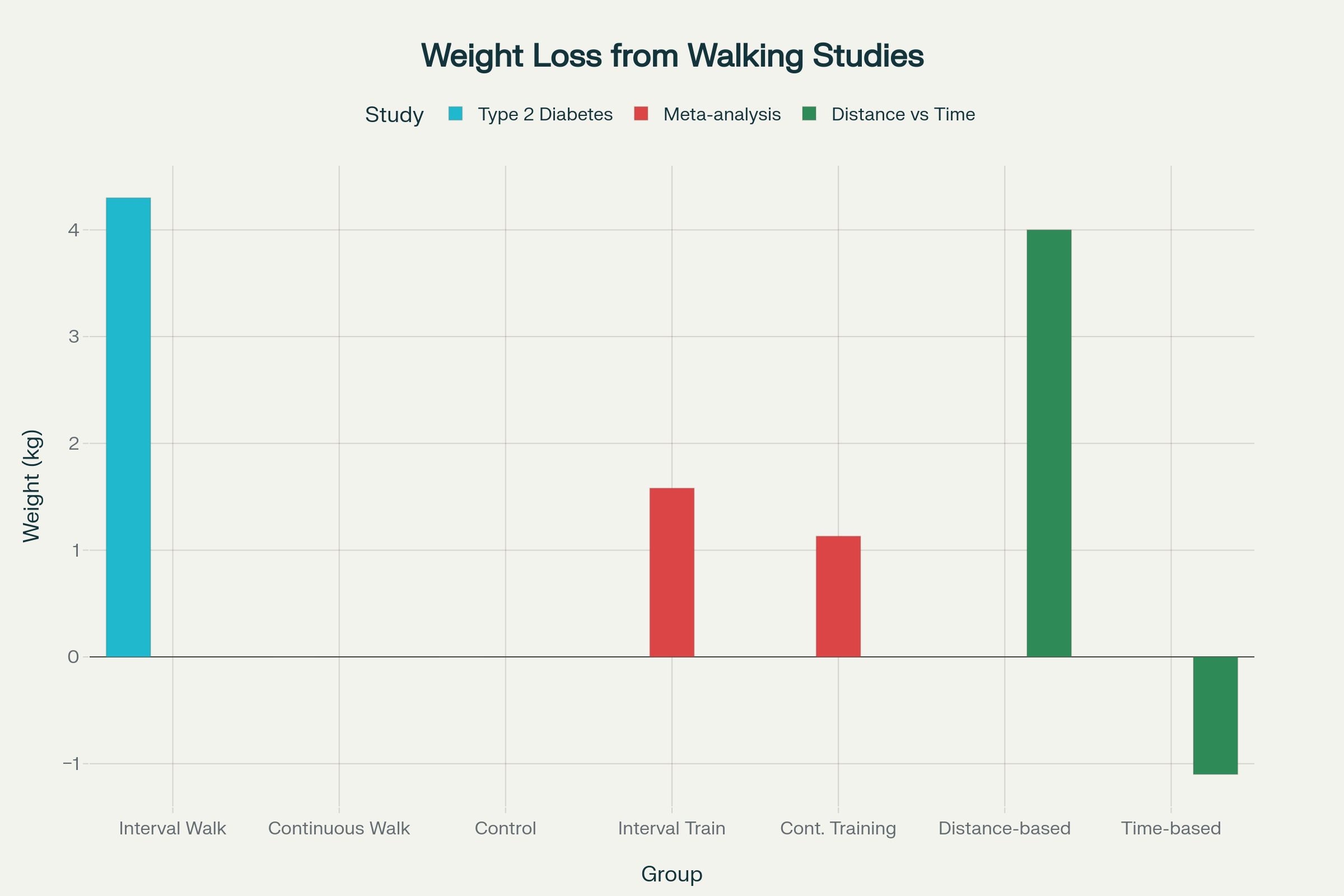
Weight Loss Results from Interval Walking Research Studies
The weight loss benefits of interval walking are supported by robust scientific evidence from multiple large-scale studies. A landmark randomized controlled trial involving participants with type 2 diabetes found that interval walking produced 4.3 kg of weight loss over four months, while participants engaging in continuous walking at the same energy expenditure showed no significant weight change. This study is particularly significant because it carefully matched the total energy expenditure between groups, demonstrating that the interval structure itself, rather than simply burning more calories, drives superior weight loss results.
A comprehensive meta-analysis published in the *British Journal of Sports Medicine* analyzed 41 studies involving over 1,000 participants and found that interval training produced an average weight loss of 1.58 kg compared to 1.13 kg for continuous exercise over similar time periods. While this difference may appear modest, it represents a 40% greater weight loss achieved through interval methods. More importantly, the study found that sprint interval training, which includes high-intensity walking intervals, was particularly effective for promoting fat loss.
Additional research reveals that the body composition changes from interval walking extend beyond simple weight reduction. The same diabetes study showed that interval walking participants lost 3.1 kg of body fat while preserving lean muscle mass, and experienced significant reductions in visceral abdominal fat. These changes are crucial for long-term health, as visceral fat reduction is associated with decreased risk of cardiovascular disease and metabolic disorders.
Physiological Mechanisms and Metabolic Benefits
The superior weight loss effects of interval walking stem from several distinct physiological mechanisms that work synergistically to enhance fat burning. During high-intensity intervals, the body rapidly depletes muscle glycogen stores, forcing it to rely more heavily on fat oxidation during recovery periods. This metabolic shift continues for hours after exercise completion, creating what researchers term the "afterburn effect."
Interval walking also stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis—the creation of new cellular powerhouses responsible for energy production. Studies show that mitochondrial capacity can increase by 23% in older adults following interval walking programs, directly enhancing the body's ability to burn fat efficiently. This adaptation is particularly significant because mitochondrial function typically declines with age, making interval walking an effective strategy for combating age-related metabolic slowdown.
The hormonal response to interval walking further amplifies its weight loss benefits. High-intensity intervals trigger increased production of catecholamines (adrenaline and noradrenaline), which mobilize stored fat and increase overall energy expenditure. Research indicates that exercise frequencies of three or more sessions per week can promote significant fat loss due to this enhanced catecholamine response.
Practical Implementation: Getting Started Safely
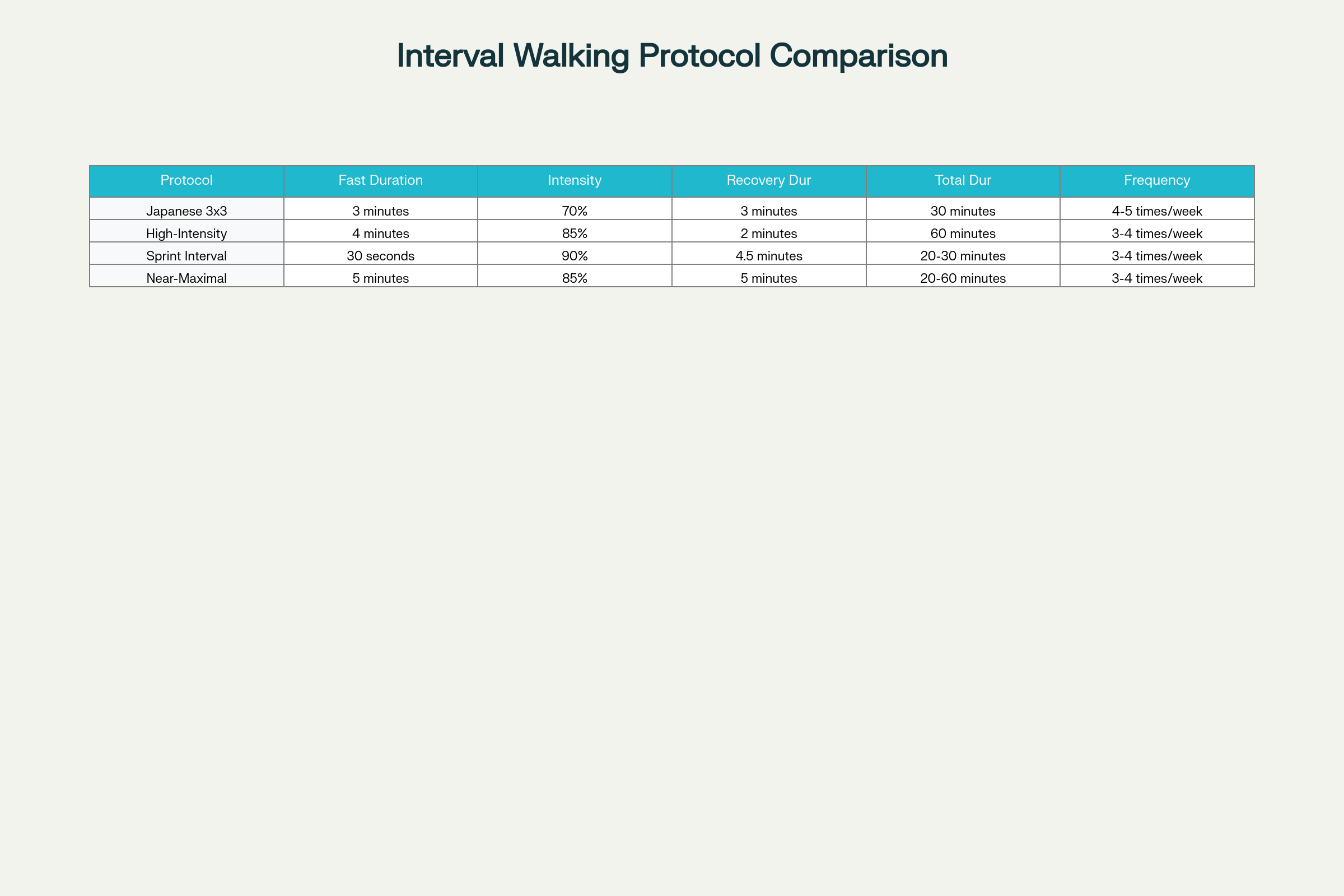
Comparison of Different Interval Walking Training Protocols
For beginners, the key to successful interval walking lies in gradual progression and proper intensity management. The most accessible starting point involves implementing a modified version of the Japanese 3x3 protocol. Begin with 2 minutes of moderate-pace walking followed by 1 minute of brisk walking, repeated for 15-20 minutes total. This allows the cardiovascular system to adapt gradually while building confidence and habit formation.
Intensity during interval walking should be gauged using the Rate of Perceived Exertion (RPE) scale, where moderate pace feels like 4 out of 10 (conversational pace) and brisk pace feels like 7 out of 10 (challenging but sustainable). At the brisk pace, you should be able to speak in short sentences but find continuous conversation difficult. This subjective approach eliminates the need for expensive heart rate monitors while ensuring appropriate intensity levels.
Safety considerations are paramount, particularly for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those who have been sedentary. Always begin with a 5-10 minute warm-up at an easy pace, and conclude with a similar cool-down period. Proper footwear is essential—invest in quality walking shoes with adequate cushioning and support. Start with 2-3 sessions per week on non-consecutive days to allow for adequate recovery, gradually progressing to the recommended 4-5 sessions as fitness improves.
Advanced Protocols and Variations

Person walking briskly outdoors on a trail in a green park, suitable for interval walking training to lose weight.
As fitness levels improve, several advanced interval walking protocols can provide additional challenges and continued progress. High-intensity aerobic interval walking involves 4-minute intervals at 85% intensity alternated with 2-minute recovery periods, typically performed for up to 60 minutes total. This protocol is particularly effective for individuals seeking to maximize cardiovascular adaptations and calorie burn.
Sprint interval walking represents the most intensive variation, featuring 30-second bursts at near-maximal walking speed (90% intensity) followed by 4.5 minutes of recovery walking. While demanding, this protocol can be completed in just 20-30 minutes and has been shown to produce comparable fitness benefits to much longer continuous exercise sessions.
For those seeking moderate intensity increases, step-wise interval walking gradually elevates intensity every 4 minutes, starting at comfortable pace and progressively increasing to challenging levels. This pyramid-style approach helps build endurance while providing variety to prevent boredom and maintain motivation.
Integration with Weight Management Strategy
While interval walking provides powerful weight loss benefits, optimal results occur when combined with appropriate nutritional strategies. Research indicates that exercise alone, regardless of intensity, produces modest weight loss compared to combined diet and exercise approaches. However, interval walking offers unique advantages that support long-term weight management beyond simple calorie burning.
The metabolic improvements from interval walking—including enhanced insulin sensitivity, improved glucose control, and increased fat oxidation capacity—create favorable conditions for maintaining weight loss. Studies show that participants following interval walking programs maintain their weight loss more effectively than those relying solely on dietary restrictions, likely due to the preservation of metabolically active muscle tissue and improved energy system efficiency.
Progressive overload principles apply to interval walking just as they do to resistance training. Gradually increase session duration, add extra intervals, or incorporate environmental challenges such as hills or weighted vests to continue advancing. The key is making small, sustainable increases that challenge the body without leading to overuse injuries or burnout.
Long-term Adherence and Sustainability
One of interval walking's greatest strengths lies in its exceptional adherence rates compared to traditional exercise programs. Research shows that 95% of participants successfully complete interval walking interventions, significantly higher than the typical 60% adherence rate for continuous walking programs. This success stems from several factors including the time-efficient nature of the workouts, the variety provided by changing intensities, and the immediate perceived benefits.
To maximize long-term success, consider incorporating social elements such as walking with friends or joining organized groups. Many communities now offer interval walking programs specifically designed around the Japanese 3x3 method. Additionally, smartphone apps can provide structure, timing cues, and progress tracking to maintain motivation and ensure proper interval execution.
The mental health benefits of interval walking—including reduced depression scores and improved cognitive function—create positive feedback loops that support continued participation. Participants frequently report increased energy levels, better sleep quality, and enhanced mood regulation, benefits that extend far beyond weight loss and contribute to overall quality of life improvements.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Path to Weight Loss
Interval walking represents a scientifically-validated, accessible, and highly effective approach to weight loss that addresses many of the barriers associated with traditional exercise programs. The Japanese 3x3 method and related protocols offer proven strategies for losing weight while improving cardiovascular health, building strength, and enhancing overall well-being. With proper implementation and gradual progression, interval walking can become a cornerstone of long-term weight management, providing sustainable results that extend far beyond simple calorie burning to encompass comprehensive metabolic and psychological health improvements.
The evidence overwhelmingly supports interval walking as superior to continuous moderate-intensity exercise for weight loss, offering 40% greater results while requiring less time commitment and creating lower injury risk. For individuals seeking an evidence-based, sustainable approach to weight management, interval walking provides an optimal combination of effectiveness, accessibility, and long-term adherence potential that makes it an ideal choice for lasting health transformation.
Comments
Post a Comment